Issue management and estimation
Good development is dependent on effective project management.
This session will introduce new concepts essencial to your project planning and management.
For more detail, you can visit these resources:
Are you familiar with all of the following concepts?
- Scrum™
- Sprint
- User story
- Backlog
- Sprint retrospective
- Project board (Kanban)
Here are some new concepts
(can you guess at their meaning?)
Estimate
Meaning:
The difficulty level of an issue
Estimates are expressed in points and represented with an E
For example: E2 meaning, an issue estimated to be a 2 in difficulty
Some teams may estimate in absolute time (where an issue will be measured in hours or days of work), others will estimate in relative time (where an issue will measured realtive to others)
In order to help understand relative estimations, we are recommending the following system:
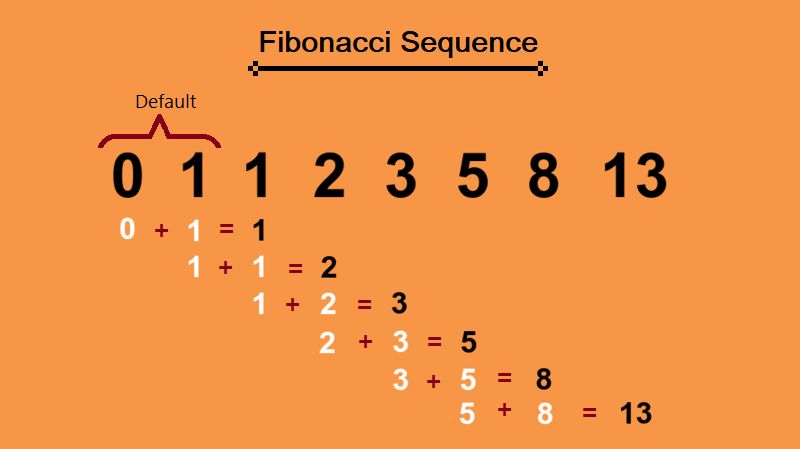
Using the Fibonacci Sequence stresses the notion that difficulty grows exponencially
- E1 is a good first issue
- E2 is an easy issue
- E3 is a medium issue
- E5 is a harder issue
- E8 is a complex issue
Actuals
Meaning:
The actual difficulty level of an issue
Actuals are calculated when an issue is closed and follow the same system as Estimates.
If an Issue was estimated as an E1 but turned out to be much more complex than expected it will have an Actual of A3 (for example)
Velocity
Meaning:
The team’s performance, expressed by the calculated difference between Estimates and Actuals
The issue from our earlier example would have a Velocity of V-2
(E1 - A3 = V-2)
Sprint backlog
Meaning:
A prioritised list of all the user stories that we estimate will be completed in the next sprint
Sprint planning
Meaning:
Where the team prioritises user stories and agrees the next Sprint Backlog
Sprint Review
Meaning:
Where the team compares their estimate with the actual number of user stories completed
RECAP
- Estimate
- Velocity
- Sprint backlog
- Sprint Planning and Review
Note
Not all issues in the project board contribute to the Velocity of your team.
Chores, Bugs, Refactors and Spikes are all considered zero-point issues and do not get assigned an Estimate.
Why do you think that is?
- Chore - is something that needs to be done but is not directly related to a user story
- Bug - is a problem in the code that needs to be fixed for the product to be viable
- Refactor - is an improvement to the code’s maintainability that does not deliver any change to user experience
- Spike - is a researching task in order to find a potential solution to a problem
Labels
All these new concepts can be (and usually are) used as labels in your Project Board
It looks something like this example
In your presentations going forward
- Report on estimated vs actual velocity
- And don’t forget to show your project board
Final thought: Hofstadter’s Law
Everything always takes longer than you expect, even when you take into account Hofstadter’s Law.